
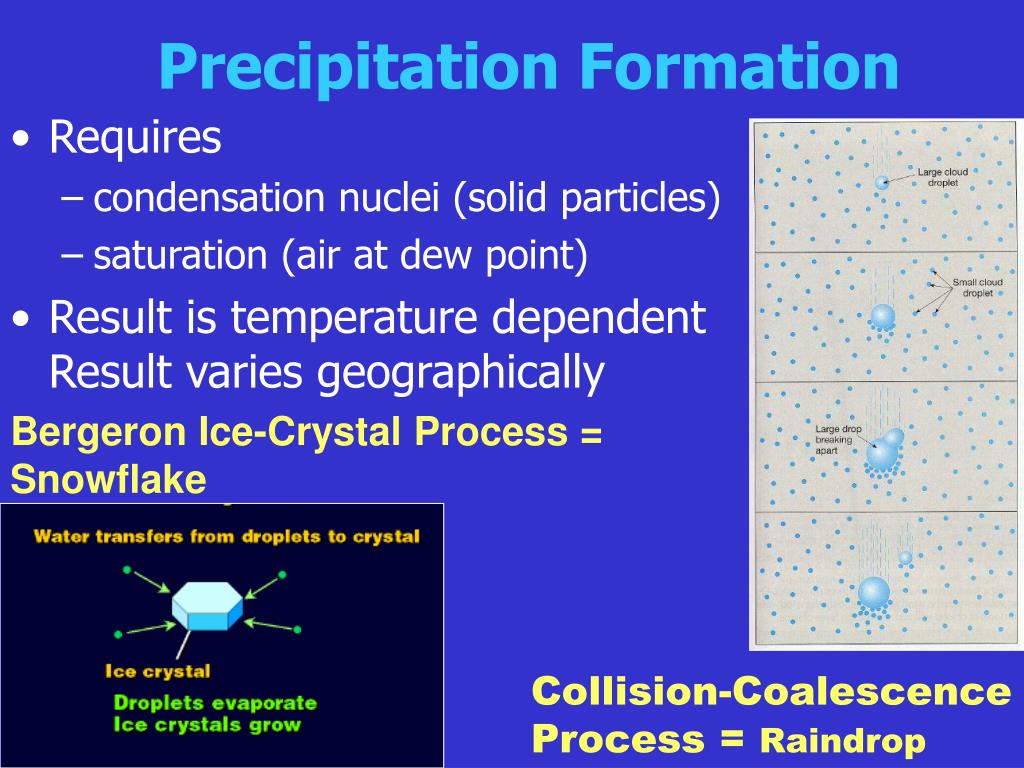
2 The next phase in the sequence comes when the experiment is left with about 20 of its original level. At this point, minor carbonates begin to form. Precipitation reactions serve important functions. The solid that forms via a precipitation reaction is called the precipitate. (Ionic salts are a good example: usually they have strong interactions in the solid and solvated states. The first phase of precipitation begins when about 50 of the original water depth remains. To precipitate is to form an insoluble compound, either by decreasing the solubility of a compound or by reacting two salt solutions. There are many other factors that can affect solubility, but these rules are a good first step. The finished reaction is: 2 KCl (aq) + Pb (NO 3) 2 (aq) 2 KNO 3 (aq) + PbCl 2 (s) The solubility rules are a useful guideline to predict whether a compound will dissolve or form a precipitate. Clastic sedimentary rocks are composed of discrete fragments or clasts. This means PbCl 2 is insoluble and form a precipitate. For instance, if it has very strong interactions between molecules or ions in the solid state, then it won't be very soluble unless the solvation interations are also very strong. These groups are clastic, chemical precipitate and biochemical or biogenic. Nitrate of Baryta, it gives a white powdery precipitate, which does not disappear on the addition of nitric or muriatic acid, the solution contains. Solubility depends on the relative stability of the solid and solvated states for a particular compound. Precipitates are insoluble ionic solid products of a reaction, formed when certain cations and anions combine in an aqueous solution. (It's also a little funny because many salts aren't strong electrolytes, so teachers might be telling their students to write an equation that doesn't show what's really happening.) However, it does help show what it means to be a spectator ion, since they are the same on both sides when you write it like this.

No real chemist would be likely to do this because it is a nuisance. These results are helpful to improve the understanding of secondary mineral and its environmental response, and are of great significance for the environmental protection and sustainable development of mining area.(aq)\]

Chert, another commonly found chemical sedimentary rock, is usually produced from silica (SiO 2) precipitated from groundwater. According to the analysis of water quality characteristics of water samples, basaluminite can reduce the ions content in the AMD and enrich Cu, Ni, Mo, Cr and F ions, showing an excellent self-purification capacity of the water body. 1: A type of chert, flint, shown with a lighter weathered crust.
#Precipitate geology software
The geochemical simulation result of the PHREEQC software verified that the white precipitate was basaluminite. Moreover, by comparing the mole number of chemical elements, the main mineral composition of the white precipitate was closest to basaluminite. For this to happen, the water body must enter a restricted environment where water input into this environment remains below the net rate of evaporation. Understanding the geological and geochemical processes that lead to precipitation, or dissolution, of calcite help us understand the chemical steps that.
The white precipitate was a kind of amorphous crystal with the characteristics of a fine powder, and its main elements were O, Al, S, F, OH− and SO42− groups. Formation of evaporite rocks Although all water bodies on the surface and in aquifers contain dissolved salts, the water must evaporate into the atmosphere for the minerals to precipitate.
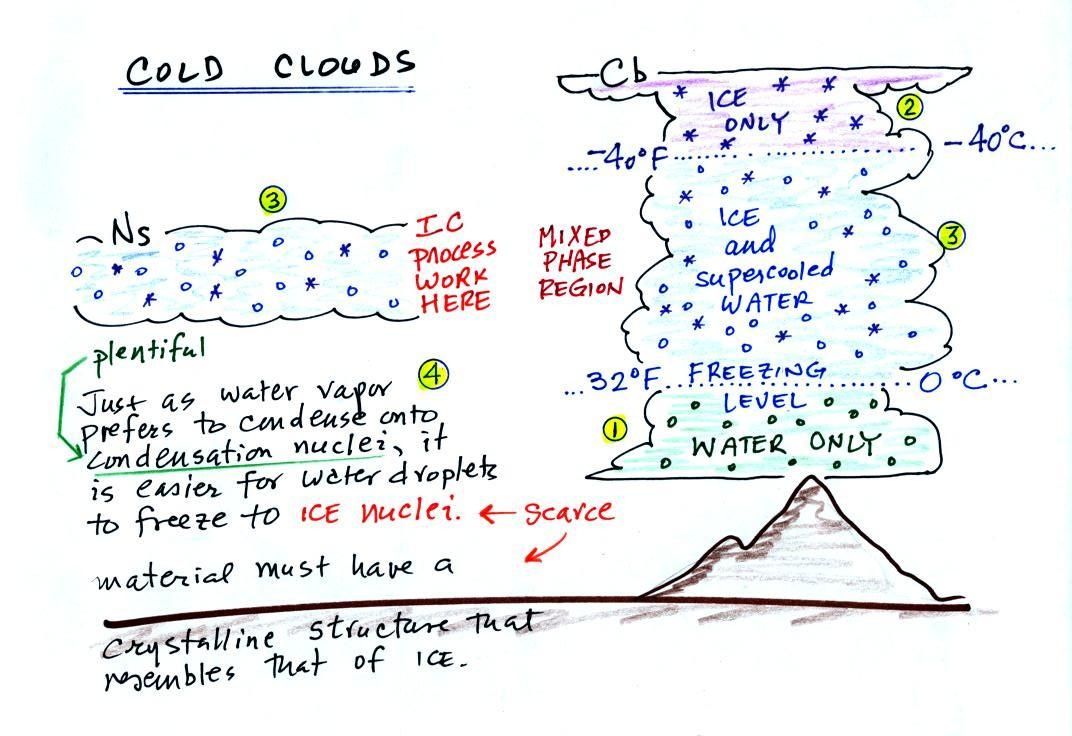
For example, the Bonneville Salt Flats in Utah flood with winter rains and dry out every summer, leaving behind salts such as gypsum and halite. Hence, when we look at marine-fed potash deposits in a framework of geological time. The precipitate minerals form various salts known as evaporites. The mineral composition of white precipitate was characterized by Scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM–EDS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT–IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometer (ICP–AES), chemical quantitative calculation and PHREEQC software. These precipitation stages define the carbonate and gypsum divides. Precipitation: It is the total supply of all forms of moisture emanating (coming) from the clouds and falling to the ground. The study focuses on the white secondary mineral precipitate and its environmental response formed in acid mine drainage (AMD) at Jinduicheng Mine (Shaanxi, China).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
